Advantages of brushless DC ferrite rotor
In the vast field of modern industry and household appliances, brushless DC motors have become an indispensable part due to their
excellent performance and wide application range. The brushless DC ferriteinternal rotor motor, with its unique structure and
advantages, has become a leader in the field of motors.
1、 The characteristics of brushless DC ferrite internal rotor motor
The brushless DC ferrite rotor motor, as the name suggests, uses ferrite material as its rotor. Ferrite has become an ideal choice for motor
rotors due to its high magnetic permeability, low magnetic resistance,and good high-temperature resistance. Compared with traditional motors,
brushless DC ferrite internal rotor motors have higher efficiency and longer lifespan.The core advantage of brushless DC motors lies in their
brushless design. Traditional brushed DC motors rely on friction between carbon brushes and commutators to achieve current commutation.
This design not only generates significant noise and wear, but also limits the speed and lifespan of the motor. Brushless DC motors, on the other
hand, precisely control the commutation of current through electronic commutators, achieving higher speeds and longer lifespans.
In addition, brushless DC ferrite internal rotor motors also have advantages such as high torque, wide speed range, high precision, and low noise.
These characteristics have made brushless DC ferrite rotor motors widely used in industrial automation, household appliances, electric tools,
automotive industry, and medical equipment.
2、 The structure of brushless DC ferrite internal rotor motor
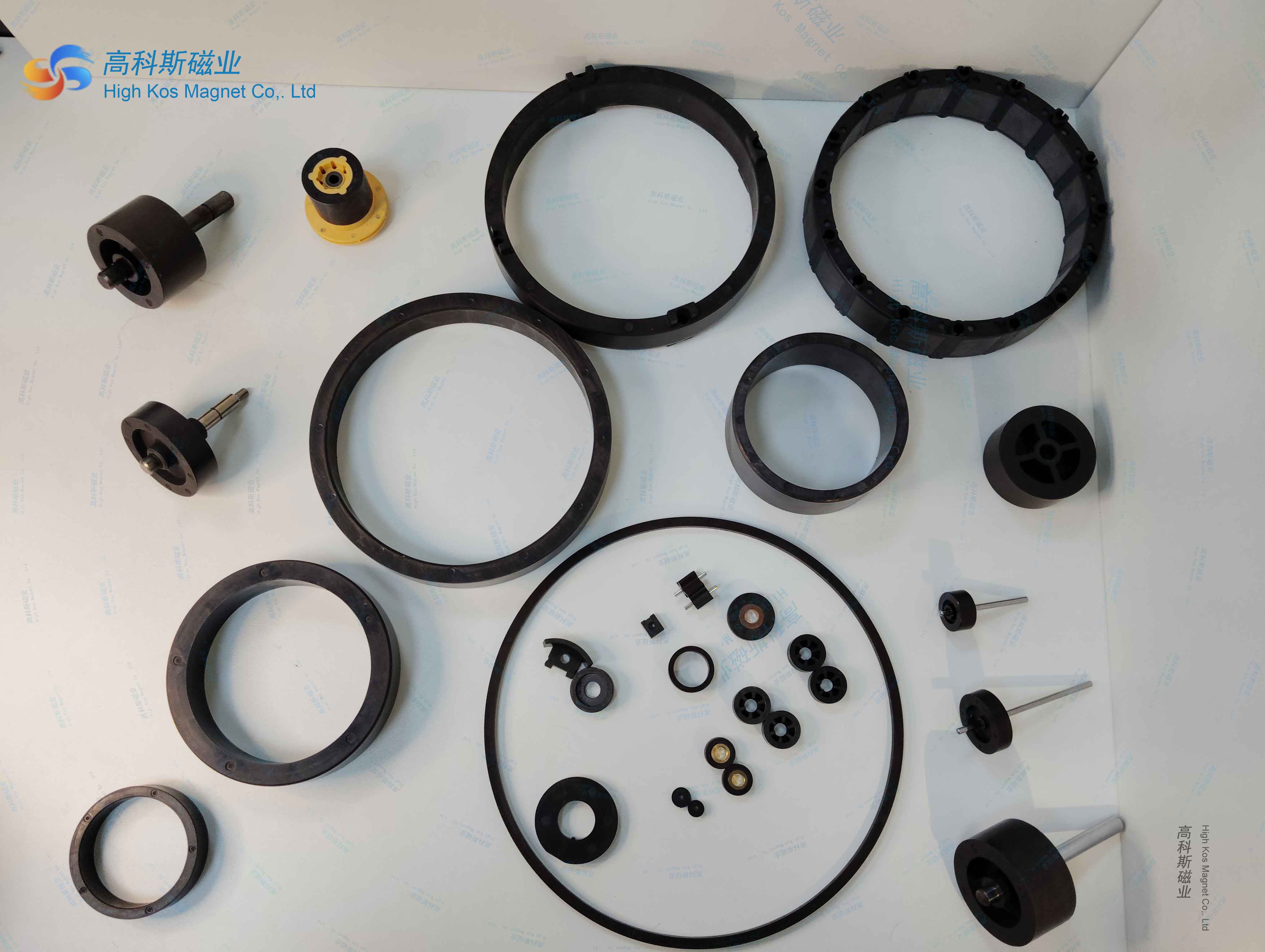
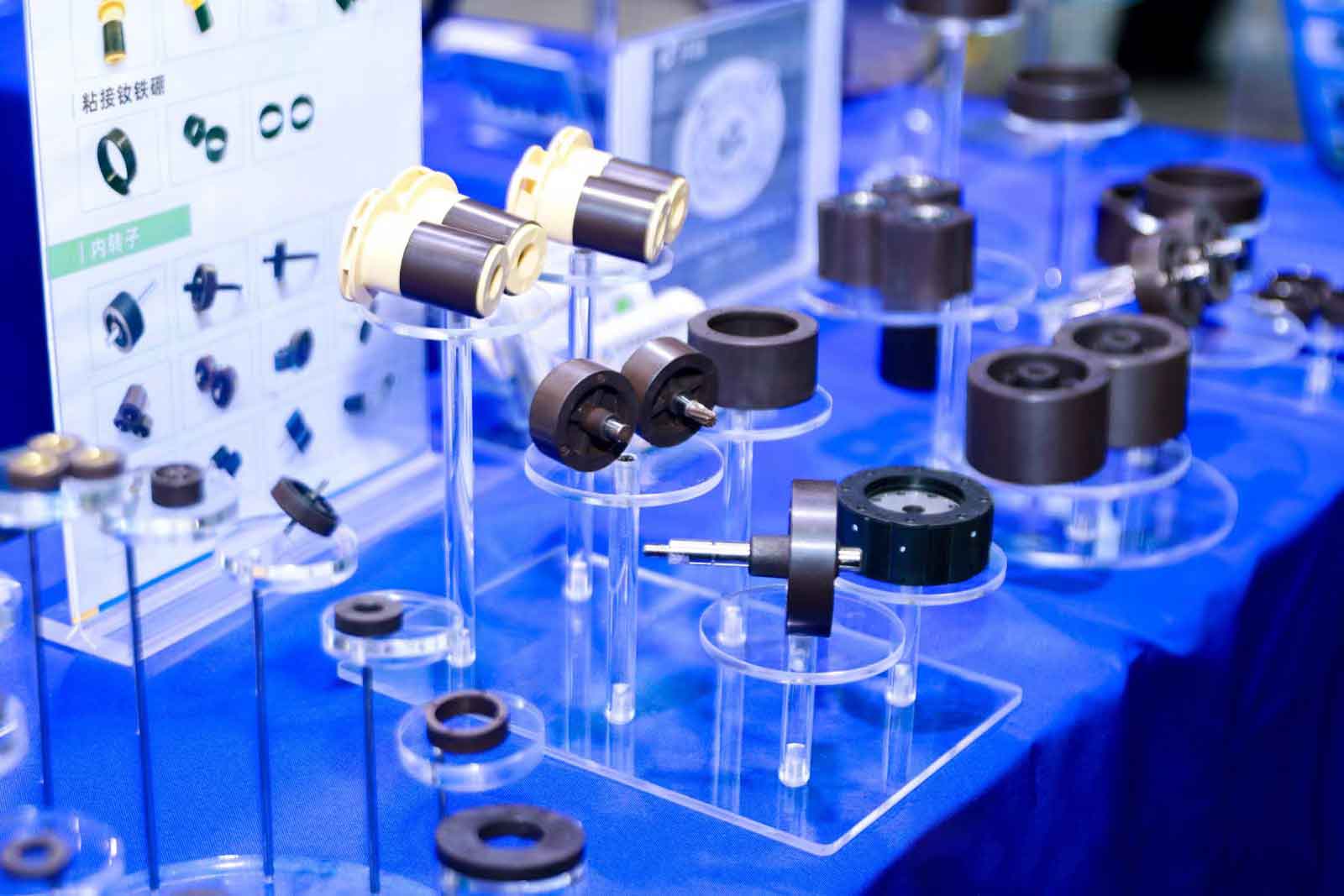
The brushless DC ferrite internal rotor motor mainly consists of a rotor, stator, sensor, and driver. Among them, the rotor is made of ferrite material
and connected to the driving device through the motor shaft,allowing the rotor to rotate. The stator is composed of multiple windings,
which further generate a magnetic field through current in the windings. Sensors are used to detect the position of the rotor, usually compo