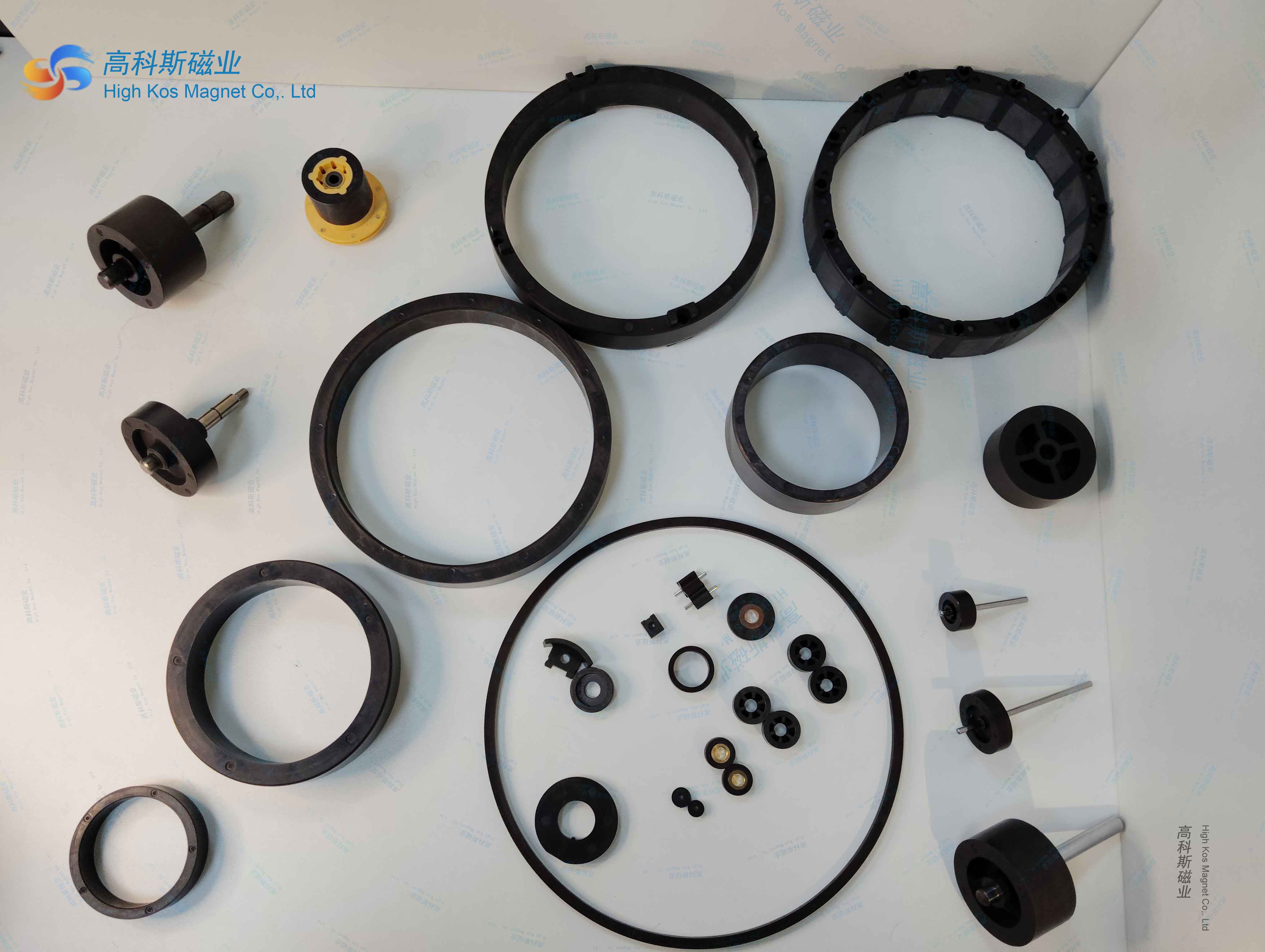
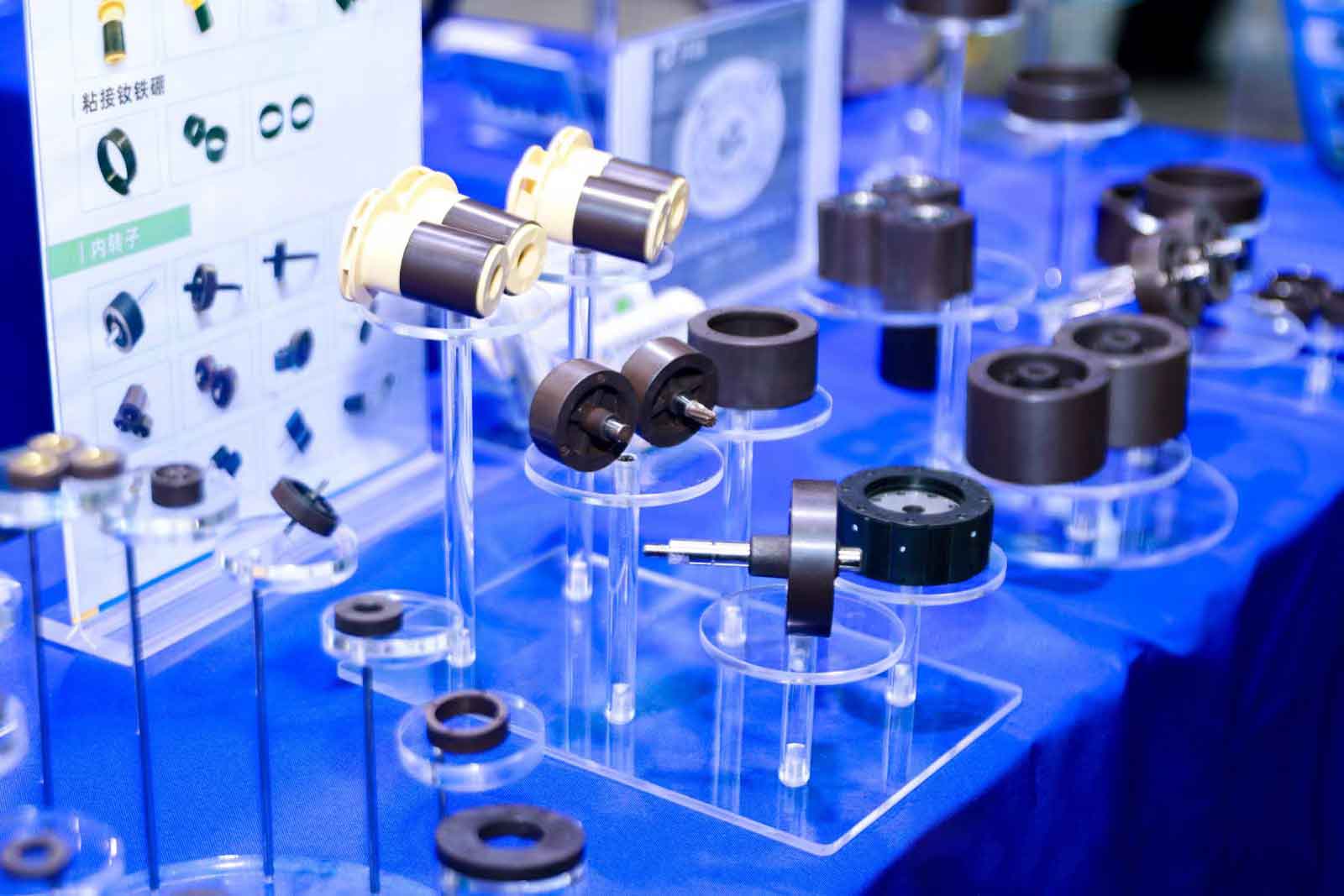
The influence of magnet thickness on fan motor
The thickness of the magnet is one of the key parameters affecting the performance of fan motors, and its changes directly affect multiple dimensions such as magnetic field strength, motor efficiency, noise, temperature rise, and cost.
1. Magnetic field strength and torque
Positive relationship:
The thickness of the magnet increases → the cross-sectional area of the magnetic circuit increases → the magnetic flux increases → the air gap magnetic field strength (B) increases → the motor output torque significantly increases.
Typical scenario: Industrial fans that require high torque (such as cooling tower fans), increasing the thickness of the magnet appropriately can improve starting performance.
Saturation risk:
When the thickness of the magnet exceeds the saturation magnetic flux density (Bs ≈ 1.8T) of the magnetic circuit material (such as silicon steel sheet), the magnetic permeability drops sharply, causing the magnetic field amplification to slow down or even become ineffective.
2. Efficiency and energy consumption
Eddy current losses:
Magnetic field enhancement → increase in iron core eddy current loss → decrease in motor efficiency, especially in high-speed fans (such as CPU cooling fans).
Copper loss optimization:
Magnetic field enhancement can reduce the current required to achieve the same torque → copper loss decreases, and the balance point between iron loss and copper loss needs to be balanced.
3. Temperature rise and heat dissipation
Magnet volume and thermal resistance:
Thickness increase → magnet volume increase → heat capacity improvement → short-term temperature rise resistance enhancement (such as instantaneous overload of car cooling fans).
Long term temperature rise risk:
Thick magnets obstruct the stator heat dissipation path → thermal resistance increases → winding temperature may exceed insulation level during continuous operation.
4. Noise and vibration
Magnetostriction effect:
Magnetic field enhancement → Silicon steel sheet magnetostrictionamplification → Increased iron core vibration → Increased electromagnetic noise, caution should be taken for household fans with high noise requirements.
Structural resonance:
Thickening of the magnet leads to changes in the distribution of rotor mass → displacement of critical speed → which may cause mechanical resonance (commonly seen in axial fans).
The thickness of the magnet has a significant impact on the performance of the wheel hub motor, mainly reflected in aspects such as power, efficiency, and speed. It's not good if the magnet is too thick or too thin. Only with an appropriate thickness can the motor be both powerful and efficient. So, when designing wheel hub motors, it is necessary to find the most suitable magnet thickness based on actual needs.