Classification and Characteristics of Injection Magnetic Materials
Classification by magnetic powder type
Ferrite injection molded magnet
Ingredients: Strontium/barium ferrite (SrFe ₁₂ O ₁₉, BaFe ₁₂ O ₁₉) as magnetic powder.
Features: Low cost, good corrosion resistance, but low magnetic energy product (BH ₘₐₓ) (usually 1-4 MGOe).
Rare earth injection molded magnets
NdFeB injection molded magnets: high magnetic energy product (5-12 MGOe), but poor temperature resistance (working temperature ≤ 150 ℃), requiring surface coating for corrosion prevention.
SmCo injection molded magnets: high temperature resistance (working temperature ≤ 250 ℃), strong oxidation resistance, but high cost.
Composite magnet: Mix different magnetic powders (such as ferrite+rare earth) to balance performance and cost.
Classification by magnetic anisotropy
Isotropic magnet: Magnetic powder is randomly distributed, with flexible magnetization direction, but low magnetic properties.
Anisotropic magnet: Applying a magnetic field during injection molding to orient the powder and significantly improve its magnetic properties (such as neodymium iron boron anisotropic magnets with a magnetic energy product of over 10 MGOe).
Classified by matrix material
Thermoplastic substrates such as nylon (PA) and polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) are easy to process and can be reused.
Thermosetting matrix: such as epoxy resin, has better temperature resistance but cannot be reprocessed after molding.
Processing advantages
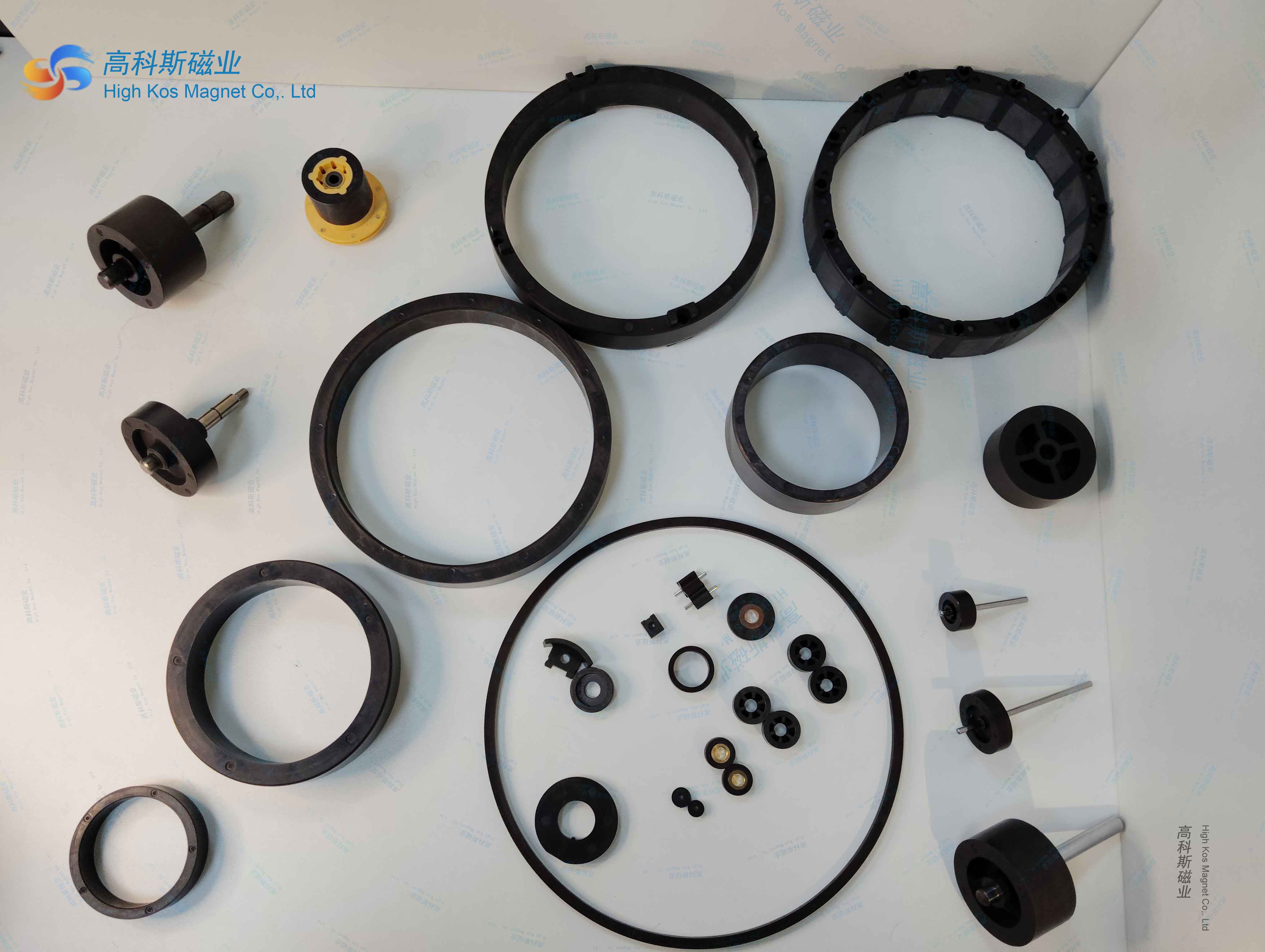
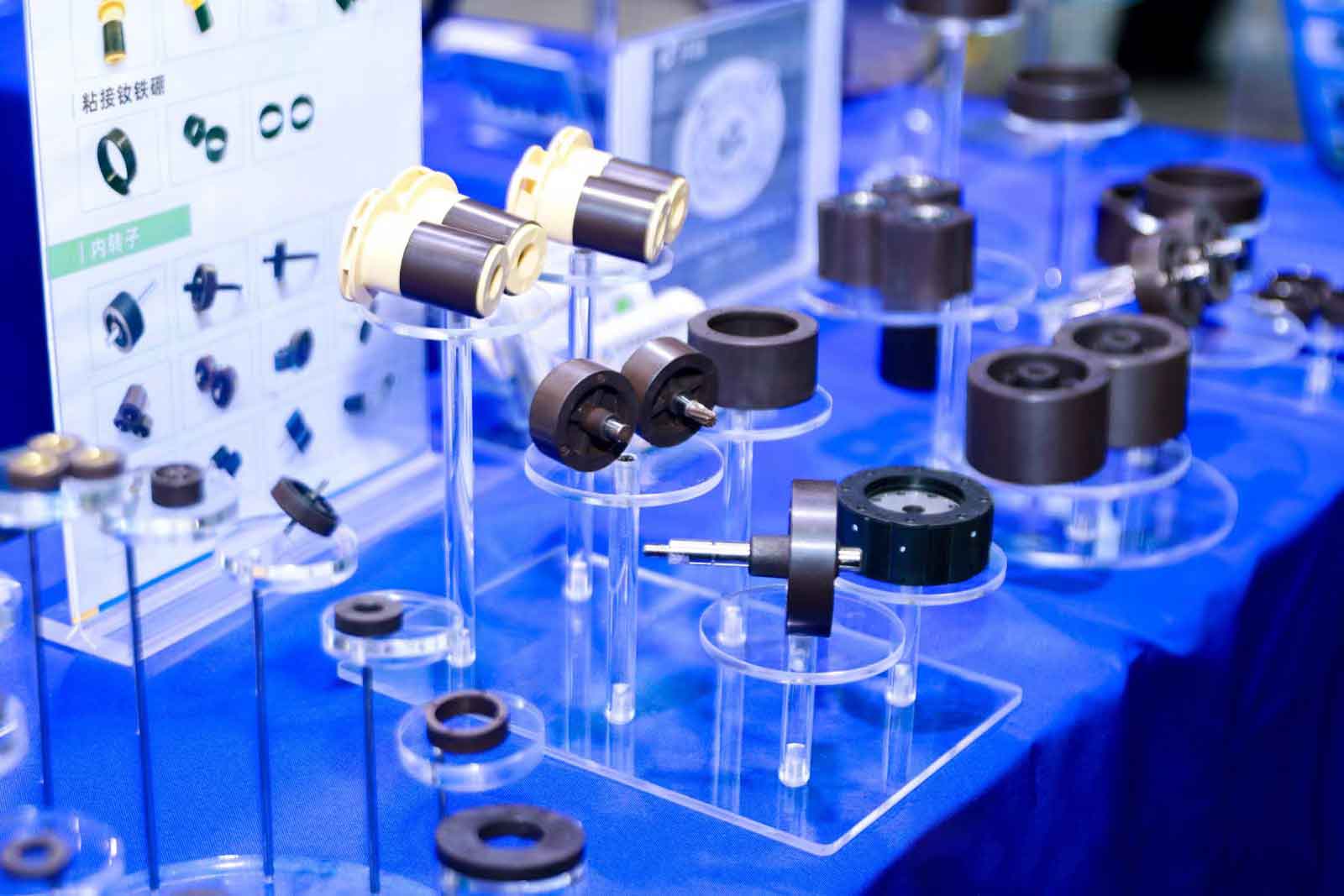
Complex shapes: can be made into thin-walled and irregular parts, suitable for precision components such as micro motors and sensors.
High precision: small dimensional tolerance (± 0.1 mm), reducing subsequent processing requirements.
Lightweight: Low density( 3–5 g/cm³), 20-30% lighter than sintered magnets.
Performance characteristics
Moderate magnetic performance: Between traditional sintered magnets and rubber magnets, suitable for medium performance demand scenarios.
Good mechanical toughness: Strong impact resistance, not easily brittle (such as neodymium iron boron injection molded magnets with a bending strength of up to 100 MPa).
Corrosion resistance: The matrix polymer can isolate the environment, especially suitable for ferrite and samarium cobalt materials.
Material selection suggestions
Low cost scenario: ferrite injection molded magnets (household appliances, toys).
High performance requirements: anisotropic neodymium iron boron injection molded magnets (precision motors, drone servos).
High temperature environment: Samarium cobalt injection molded magnets or PPS matrix materials (automotive engine peripheral components).